Cognitive Development Courses
Introduction
The Cambridge Cognitive Development courses are courses designed to improve and develop children’s cognition. The courses are based upon research into on how children’s cognition develops and how best to improve critical thinking and communication skills. Using special tasks in key domains of language, cognition, and perceptual development, our framework presents principles and strategies for both immersive and interventionist support.
In the past 20 years, research has uncovered a vast amount of information about how children learn and how best to facilitate it. Our framework accurately reflects this research which we use in the field of cognitive development as well as in the practise of a broad range of tests such as School entrance exams, Cat 4, and other cognitive assessment tests.
A fundamental consideration in our approach is being responsive to the competencies, experiences, interests, and needs of each child as a starting point. Once various fundamentals are established, practise through specially designed tasks stimulates the cerebral cortex, the brain area responsible for learning, reasoning, memory, thinking, language, emotion, intelligence, problem solving and many others. This practise is of the utmost importance for brain development and is applied in the following key areas:
1.Verbal Reasoning:
Verbal reasoning measures the ability to understand and reason with concepts and language-based information, including vocabulary, analogies, and word relationships.
<Example>

2.Non-Verbal Reasoning:
Non-verbal reasoning measures the ability to solve problems and understand patterns without relying on language. It often involves tasks such as recognizing shapes, patterns, and sequences.
<Example>
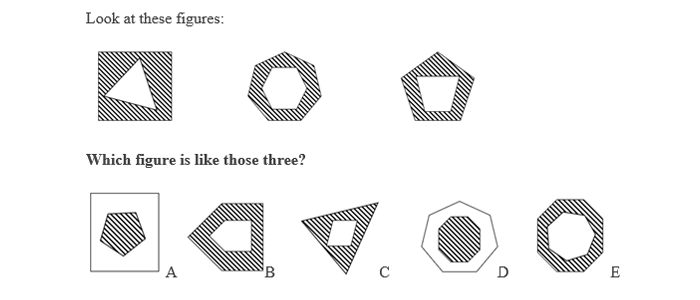
3.Quantitative Reasoning:
Quantitative reasoning assesses mathematical thinking, including the ability to analyze number patterns and work with numerical relationships and concepts.
<Example>

4.Spatial Ability:
Spatial focuses on understanding and reasoning with shapes and spatial relationships. It is often tested through puzzles or tasks that involve rotating shapes or understanding how different parts fit together.
<Example>
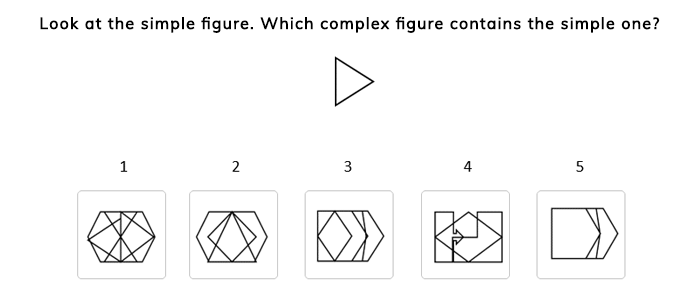
Cognitive Development
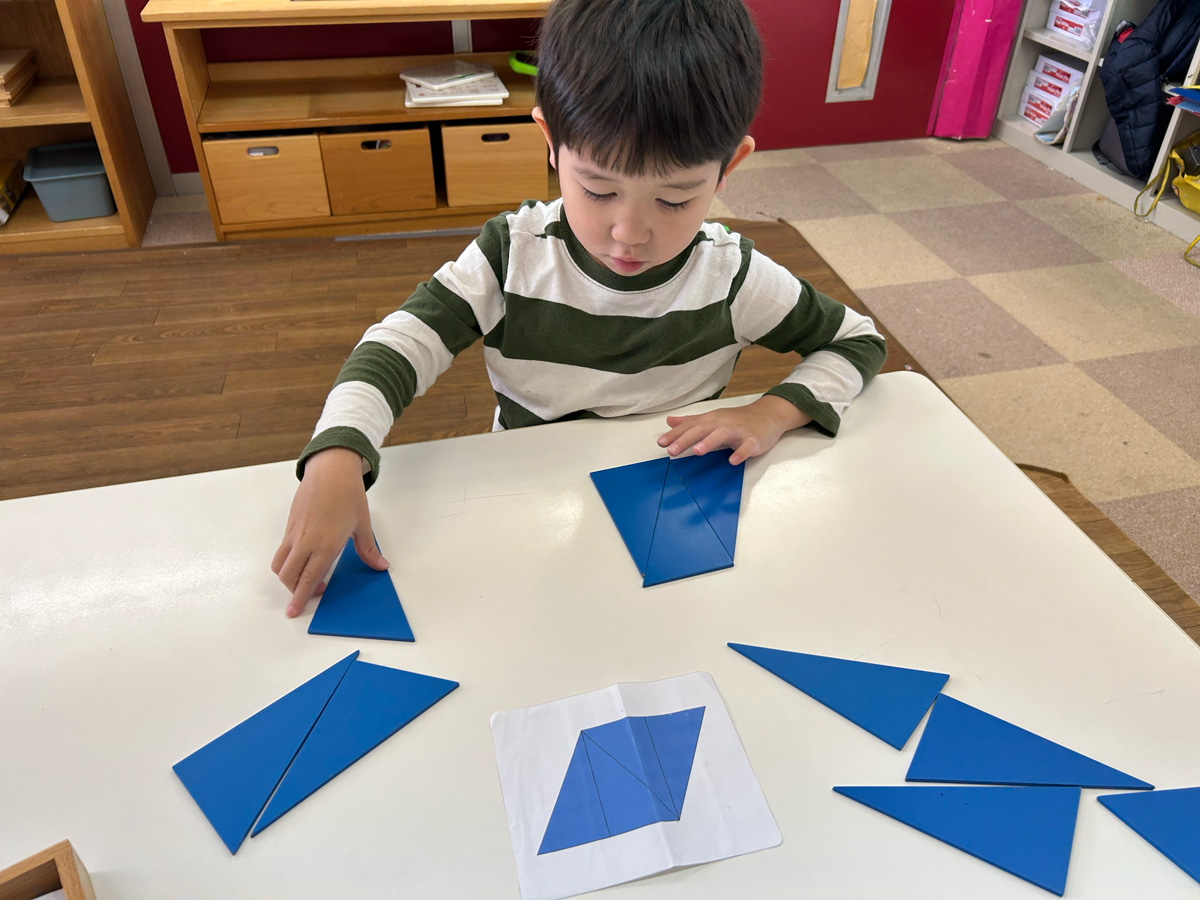
The term cognitive development refers to the process of change in intellectual or mental capabilities such as thinking, reasoning, and understanding. The cognitive tasks we want the children to undergo are those that require mental processing to acquire and organise new information. Some of these tasks involve classification and sorting, pattern recognition, cause and effect, shapes and spatial relationships, and attention and memory.
All these types of tasks promote inquiry by noticing and storing information and then using that new information in some way. For example, children can learn pattern recognition by looking at shapes in a series to determine what comes next based on the qualities the shapes possess. They need to ascertain those qualities, hold those in mind, then reason what comes next.


Developmental Milestones
Based on current research, we have designed a program that helps determine the key developmental milestones that children need to reach their full potential. These developmental milestones are the building blocks you need to get to the next stage and a central purpose of measuring whether these milestones have been met is to prevent, or limit, growth delays with targeted effective interventions.
If everything is delayed it becomes more difficult for children to perform the tasks that they’re meant to do at that age. Once children start to engage, if you give them the nourishment they need, they start growing, developing, and they catch up and go back to normal. This is true for all aspects of development milestones, it’s necessary to take steps; to intervene and to fix it problems. The concern is if those interventions are not happening.
What is the CAT4 Test?
The Cognitive Abilities Test (or CAT4) is a cognitive test developed to support schools in the understanding of students’ individual abilities and academic potential. The CAT4 is widely used as an entrance exam to many private and public schools around the world, as grade placement, as well as to select for gifted child programmes.
Cognitive Abilities Tests go beyond SATs by measuring the areas of reasoning that are known to make a difference to learning designed to give you a picture of students’ potential for achievement.
Here's a breakdown of what the CAT4 test is:
•CAT4 is a standardized test designed to assess a student's cognitive abilities across different areas, and on how well students process information, think critically, and solve problems.
•It is often used in primary and secondary education settings, from ages 6 to 17, and is typically administered to students at the beginning of a school year or when transitioning to a new school.
 Take the next step in your child’s education
Take the next step in your child’s education
Cambridge School offers online and in-person classes in English, math, and test prep. Unlock your potential using our tailored and comprehensive courses.
With our courses you can boost your skills and prepare for specialised tests such as Eiken, IELTS, and Cambridge tests. All our instructors are qualified to provide expert tuition and support for your child. Courses are available for ages 4 to 16.
Contact Us
Cambridge School

Either Japanese or English is acceptable
Weekdays from 9:00 a.m. to 6:30 p.m


